Tools
Our Tools section includes several useful modules that can enhance your .
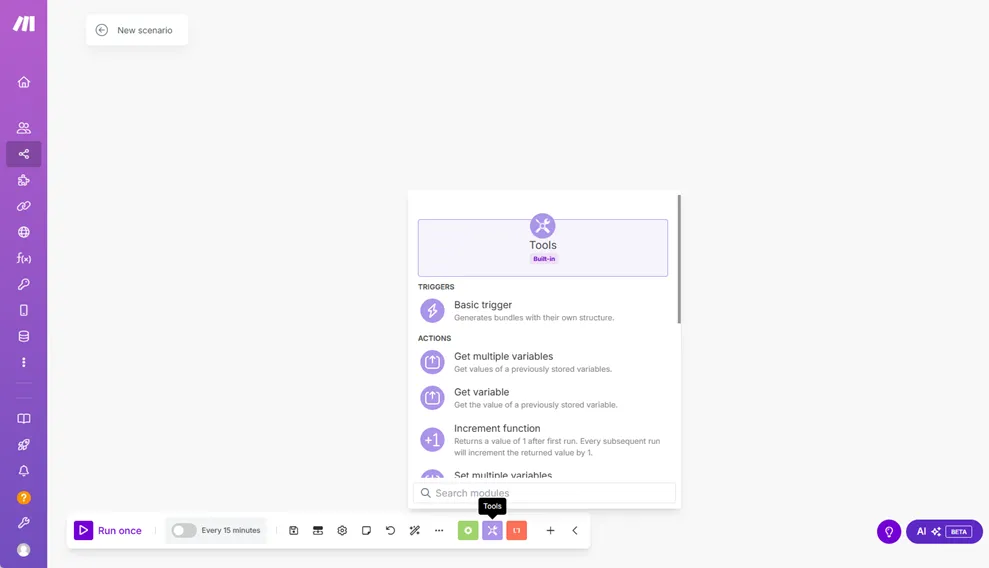
Allows you to create a custom trigger and define its input bundles.
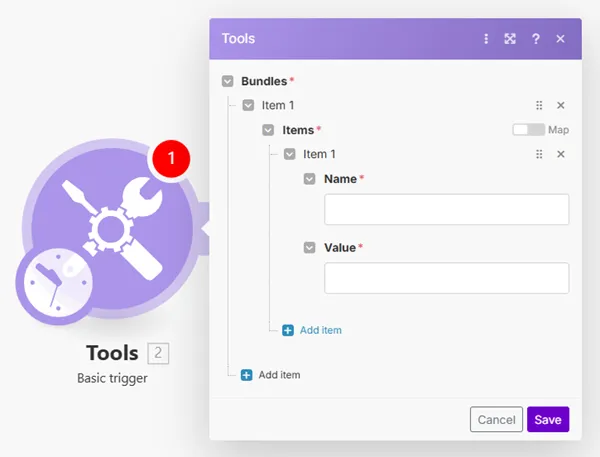
Create custom bundles by adding array items. The array consists of the name-value pairs.
For example, you can use this tool for contacts or any other list that is scheduled to be sent to a specified email address (Email > Send an Email, Gmail > Send an Email modules), or as a simple reminder to be triggered whenever it is necessary.
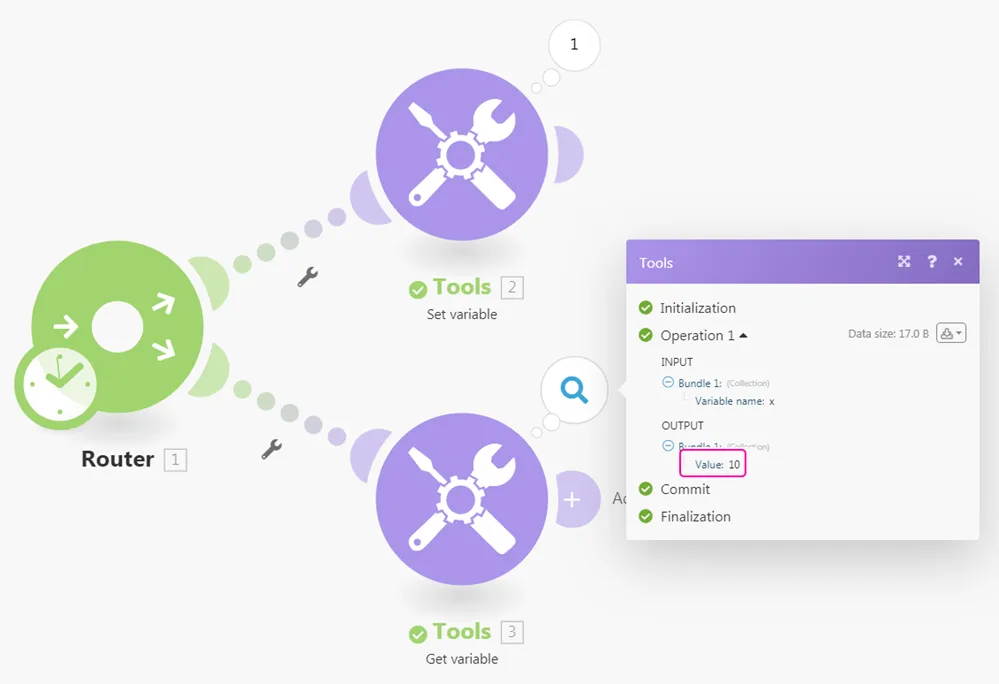
Retrieves values that were previously created by the Set multiple variables module within a single operation.
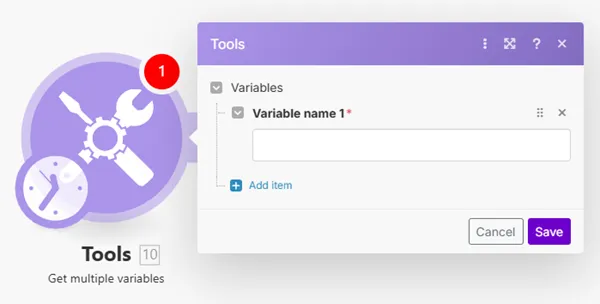
The main benefits of the Set multiple variables module are:
- one Get multiple variables module consumes just a single operation.
Retrieves a value that was previously created by the Set variable module.
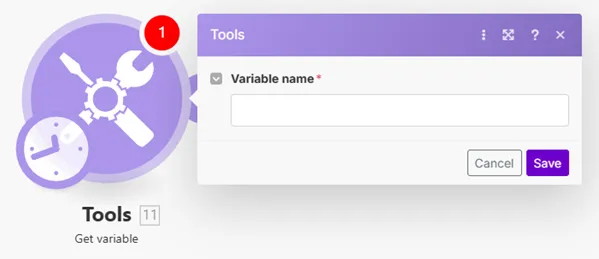
Note that this module can read a variable that was set anywhere in the . The only requirement is that the Tools > Set Variable module is executed before (in time) the Tools > Get Variable module. See the documentation for the Router module for information about the order in which routes are processed.
See our template Controlled distribution of data flow for an example of the increment function tool.
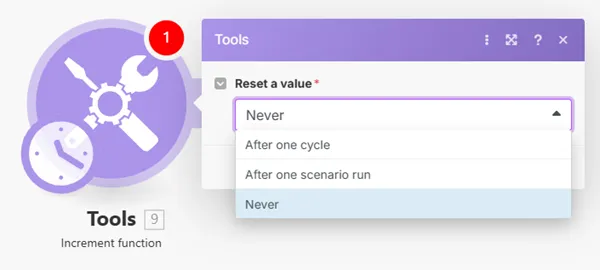
Returns a value incremented by 1 after each module's operation. It is possible to configure the module to reset the value.
One of this tool's uses is to implement a round robin assignment of tasks to users in a group. The algorithm chooses the assignees from a group in some rational order, usually going from the top to the bottom of a list and then repeating until finished (like you would deal a deck of cards).
The following sends an email to the first recipient after every odd run, and to the second recipient after every even run.

Configure the module to never reset the value:
Add a router.
Set the first condition after the router:
Odd - use the mod math function set equal to 1.

Do not forget to change the Equal to operator from the default Text operator to the Numeric operator.

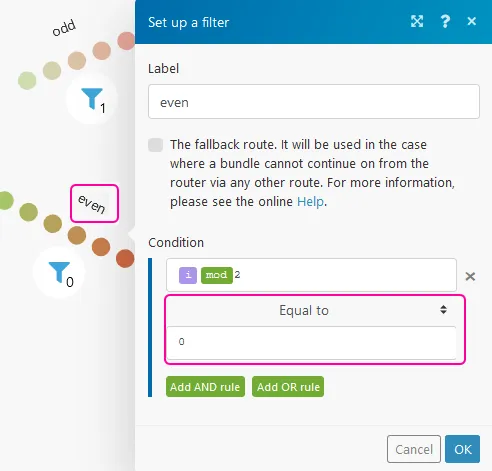
Set the second condition after the router.
Even – use the mod math function that equals 0:
Creates multiple variables that can be mapped by other modules in the route or by the Get Multiple Variables module for every route in the within a single operation.
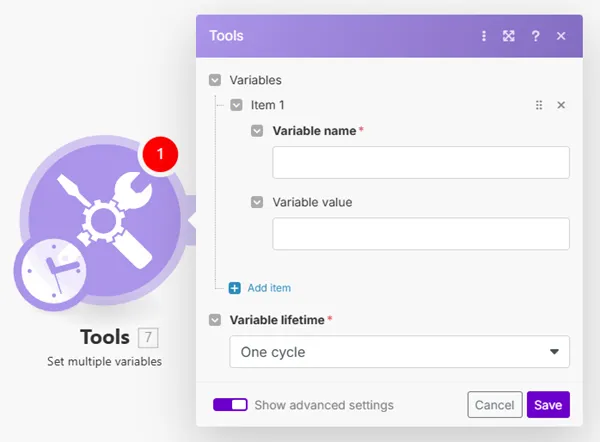
The main benefits of the Set multiple variables module are:
- one Set multiple variables module consumes just a single operation
| |
|---|---|
Variables | Add multiple variables you want to set.
|
Variable lifetime | One cycle : the variable is valid only for one cycle. Useful when multiple webhooks in one run are received (more webhooks = more cycles). One execution: The variable is valid for one execution. One execution can contain more cycles. |
Creates a variable that can be mapped by other modules in the route or by the Get variable module for every route in the .
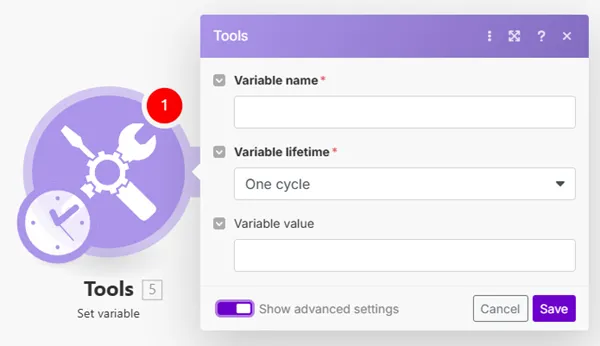
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Variable name | Enter the variable name. This name will be displayed when mapping the variable in other modules. |
Variable lifetime | One cycle : the variable is valid only for one cycle. Useful when multiple webhooks in one run are received (more webhooks = more cycles). One execution: The variable is valid for one execution. One execution can contain more cycles. |
Variable value | Enter the value of the variable. |
Allows you to delay the flow for up to 300 seconds (5 minutes).
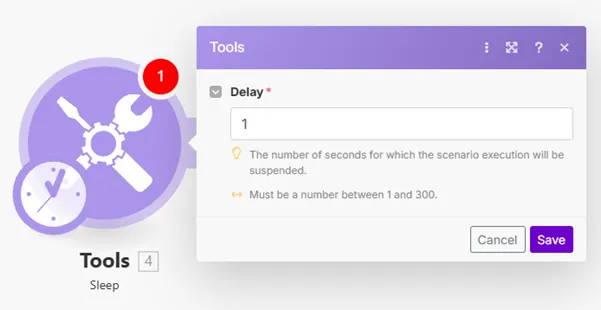
This function can be useful, for example, if you want to lower the target service server load or to simulate more human behavior when sending bulk SMS or emails.
If you wish to pause the flow for longer periods of time, we suggest splitting your into two .
- The first would contain the part before the pause.
- The second would contain the part after it.
The first would store all the necessary information in a data store together with the current timestamp. The second would periodically check the data store for records with a timestamp older than the intended delay, retrieve the records, finalize the processing of the data, and remove the records from the data store.
Allows you to retrieve numerical values, then apply one of the selected functions (SUM, AVG, COUNT, MAX,...), and return the result in one bundle.
In this example, the module sums up values under the number parameter.

Merges values from the selected fields of received bundles into a single bundle using a specified column and row separator, allowing you to create a table.
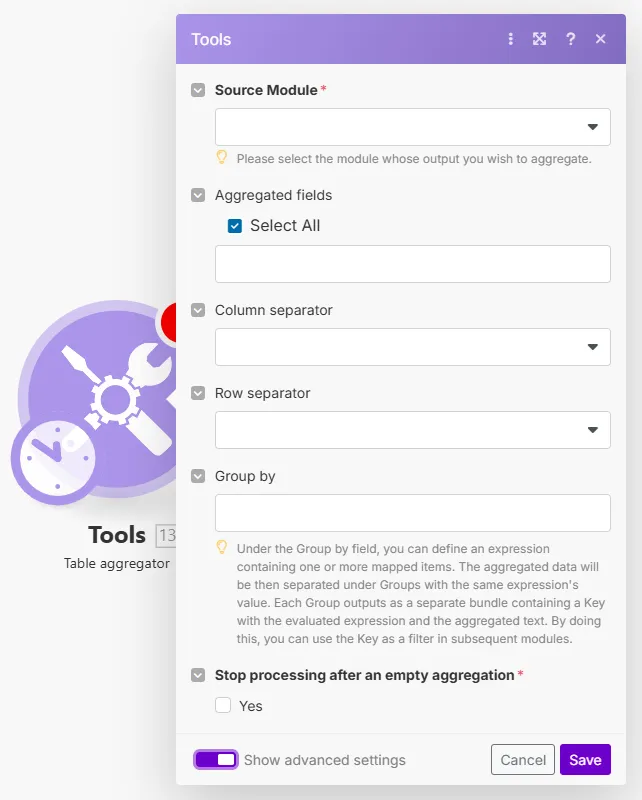
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Source module | Select the module you want to aggregate fields from. |
Aggregated fields | Select the fields from the module selected above whose values you want to aggregate into one bundle. |
Column separator | Select or enter the type of separator that will separate the field value columns in the resulting bundle. |
Row separator | Select or enter the type of separator that will separate the field value rows in the resulting bundle. |
Group by | Define an expression containing one or more mapped items. The aggregated data will then be separated into groups with the same expression's value. Each group outputs a separate bundle containing a key with the evaluated expression and the aggregated text. By doing this, you can use the key as a filter in subsequent modules. |
Merges values from the selected fields of received bundles into a single bundle.
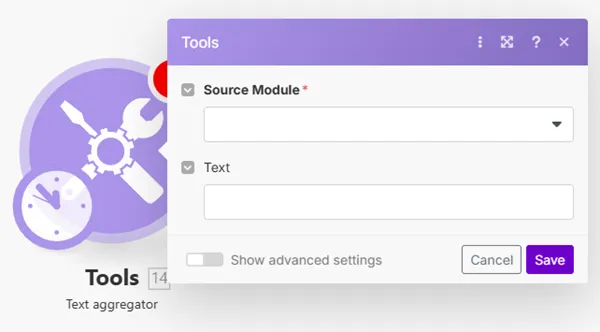
You can use the text aggregator tool to insert more values (e.g. customer names or notes) into a single bundle and send an email containing all the values in the email body or the email subject.
Converts any value to a string data type (text), making the mapping easier when mapping, for example, binary data.
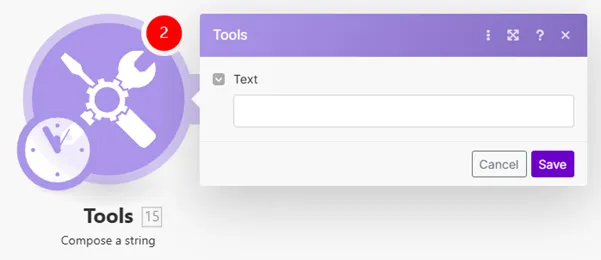
Converts entered input text (or binary data) to the selected encoding.
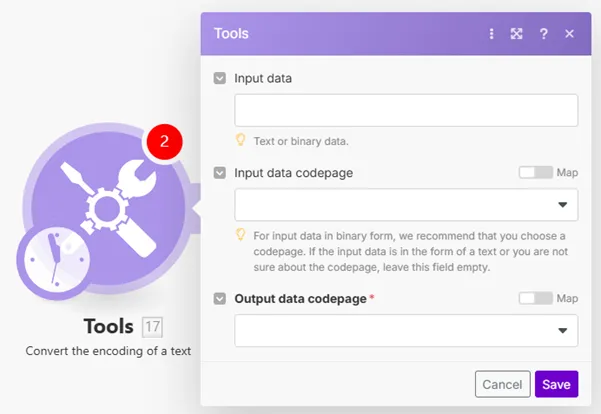
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Input data | Enter the content you want to convert. |
Input data codepage | Enter the input data encoding type. This is important for the binary form of data. |
Output data codepage | Select the target encoding of your data. |
Checks the input value for a match with the provided list of values. Returns output based on the result.
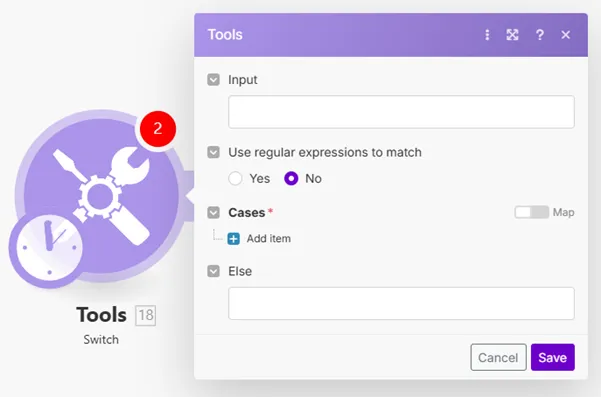
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Input | Enter the expression you want to evaluate. |
Cases | If the Input contains a value entered to the Pattern field, then the value entered to the Output field is returned. If the condition is not met, then no output is returned OR the value from the Else field (below) is returned. When using regex patterns, make sure to adhere to the ECMAScript flavor. |
Else | Enter the value that is returned when the criteria set in the Cases field is not met. |